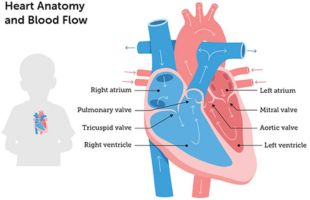
What is Coronary Angiography?
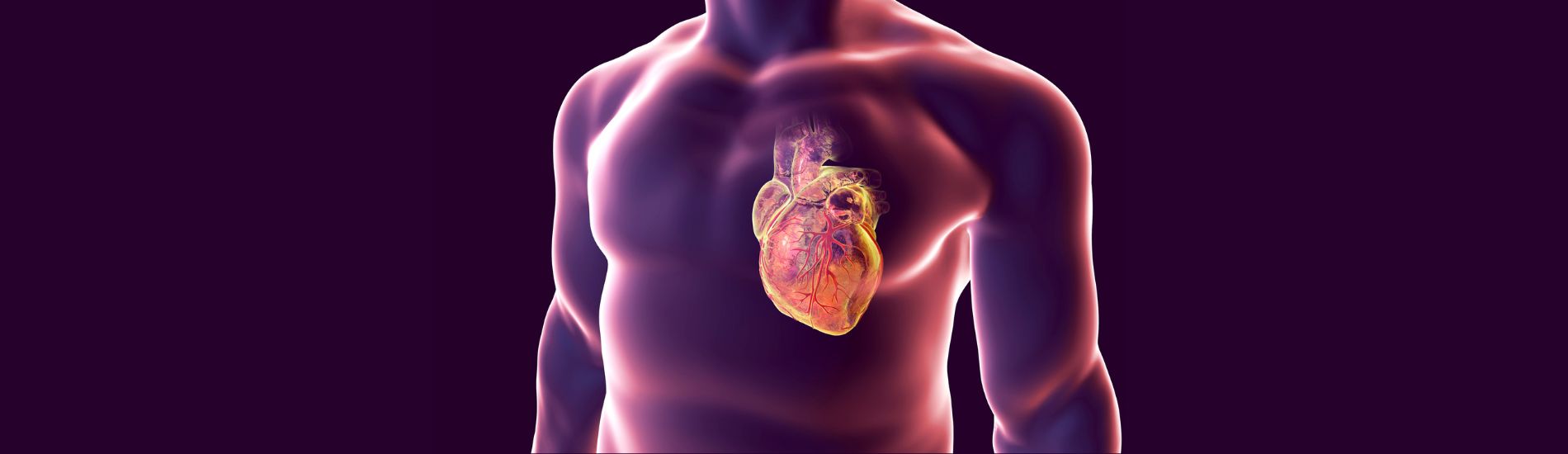
Coronary angiography is a diagnostic procedure crucial for visualizing the coronary arteries, the vital vessels supplying blood to the heart muscle. This procedure aids in precise diagnosis and treatment planning for various cardiac conditions.
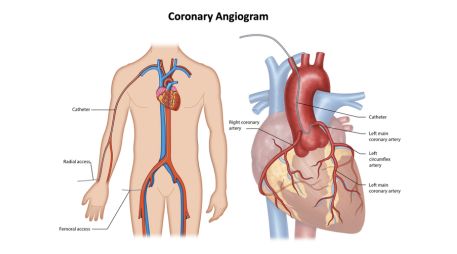
Procedure Overview:
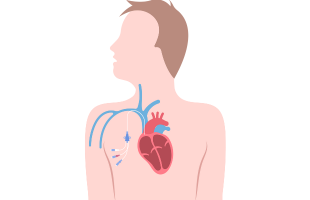
1. Involves the insertion of a catheter into blood vessels, usually in the groin or wrist.
2. Contrast dye is injected through the catheter, rendering the coronary arteries visible on real-time X-ray images.
3. Provides detailed information about the condition, size, and potential blockages within the coronary arteries.
Diagnostic Significance:
1. Essential for identifying blockages, narrowing, or abnormalities in the coronary arteries.
2. Enables healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about the appropriate treatment course.
3. Often a precursor to interventions like angioplasty or stent placement, aiding in treatment planning.
Risk Considerations:
1. Generally safe, with minimal risks such as bleeding or an allergic reaction to the contrast dye.
2. Benefits of accurate diagnosis and treatment planning outweigh potential risks.
3. Conducted under the expertise of skilled medical professionals in a controlled environment.