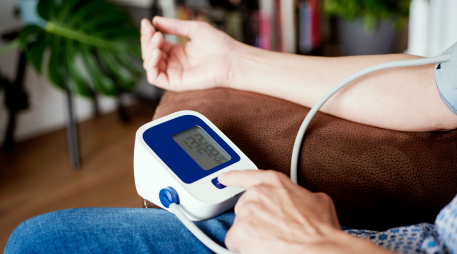
Test to check yourself
Regular testing is crucial for monitoring heart health and preventing heart diseases. Two types of tests, home tests and hospital tests, play distinct roles in this regard. A home test, such as a blood pressure monitor or a portable ECG device, provides convenience and allows individuals to monitor their heart health regularly in the comfort of their homes. These tests are useful for detecting early signs of issues and promoting preventive measures. On the other hand, hospital tests, like cholesterol screenings, stress tests, and cardiac imaging, provide a more comprehensive evaluation conducted by medical professionals. These tests are essential for a thorough examination, accurate diagnosis, and the development of appropriate treatment plans. Combining both home and hospital tests ensures a well-rounded approach to maintaining heart health and preventing potential cardiovascular diseases. Regular monitoring empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards a heart-healthy lifestyle.
1. Home tests
Home tests for heart health offer a convenient and accessible means for individuals to monitor their cardiovascular well-being. Devices such as blood pressure monitors, portable ECG machines, and cholesterol test kits empower people to take charge of their health from the comfort of their homes. Regularly measuring blood pressure allows for the early detection of hypertension, a major risk factor for heart diseases. Portable ECG devices enable individuals to record their heart's electrical activity, providing insights into irregularities. Cholesterol test kits allow for the assessment of lipid levels, aiding in the management of cholesterol-related concerns. These home tests not only offer convenience but also promote early intervention and a proactive approach to maintaining heart health. However, it's crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for a comprehensive evaluation and interpretation of results.
2. Tests In Hospitals
Hospital-based tests are instrumental in providing a thorough evaluation of cardiovascular health under the guidance of medical professionals. Comprehensive screenings, such as cholesterol tests, stress tests, and cardiac imaging, play a pivotal role in diagnosing and managing heart conditions. Cholesterol screenings assess lipid levels, aiding in the identification of potential risks. Stress tests measure the heart's response to increased workload, offering insights into its performance under different conditions. Cardiac imaging techniques, including echocardiograms and angiograms, provide detailed visualizations of the heart's structure and blood vessels. These hospital tests are crucial for accurate diagnoses, allowing healthcare professionals to tailor effective treatment plans. It's essential to recognize the complementary roles of home and hospital tests for a holistic approach to heart health maintenance.
A. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
This imaging technique provides detailed pictures of the heart's structure, helping diagnose heart conditions, assess heart function, and identify potential issues.
B. Nuclear Stress Test
The Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a vital diagnostic test conducted in hospitals to assess the electrical activity of the heart. This non-invasive procedure involves placing electrodes on the skin to record the heart's electrical impulses, providing valuable information about its rhythm and overall function. ECG tests are essential in detecting various heart conditions, such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and abnormalities in the heart's chambers. The results help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about patient care, guiding them in the development of appropriate treatment plans tailored to the individual's cardiovascular health.
C. ECG
The Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a vital diagnostic test conducted in hospitals to assess the electrical activity of the heart. This non-invasive procedure involves placing electrodes on the skin to record the heart's electrical impulses, providing valuable information about its rhythm and overall function. ECG tests are essential in detecting various heart conditions, such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and abnormalities in the heart's chambers. The results help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about patient care, guiding them in the development of appropriate treatment plans tailored to the individual's cardiovascular health.
D. Holter monitoring
Holter monitoring is a specialized test conducted in hospitals to track the heart's electrical activity continuously over a 24 to 48-hour period. During this time, a small, portable device known as a Holter monitor is attached to the patient's chest with electrodes. This monitor records the heart's electrical signals, providing a comprehensive analysis of the heart's rhythm during the individual's daily activities. Holter monitoring is particularly useful in detecting intermittent or sporadic cardiac arrhythmias that might not be captured in a standard ECG. The collected data assists healthcare professionals in diagnosing irregularities and tailoring appropriate treatment plans to address the patient's specific cardiovascular needs.
E. Echocardiography
Echocardiography, commonly referred to as an echo, is a crucial diagnostic test performed in hospitals to assess the structure and function of the heart using ultrasound technology. This non-invasive procedure involves the use of high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the heart's chambers, valves, and surrounding structures. Echocardiograms provide valuable information about the heart's size, shape, and pumping ability, aiding in the diagnosis of various cardiovascular conditions such as heart failure, valve disorders, and congenital heart defects. The real-time images generated during an echocardiogram help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about patient care, guiding treatment plans and interventions based on the specific cardiac findings.
F. CT Coronary Angiography (CTCA)
CT Coronary Angiography (CTCA) is an advanced imaging technique employed in hospitals to visualize the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle. This non-invasive procedure utilizes computed tomography (CT) technology to produce detailed, cross-sectional images of the coronary arteries, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the presence of blockages or narrowing. CTCA is particularly valuable for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD) and evaluating the overall condition of the heart. It provides a comprehensive view of the coronary vessels, aiding in the identification of potential issues like atherosclerosis or arterial stenosis. While not a replacement for traditional invasive angiography, CTCA serves as an effective and less invasive tool in the initial assessment and management of coronary artery-related concerns, contributing to timely and accurate diagnoses.
G. Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography is a diagnostic procedure performed in hospitals to visualize the coronary arteries, the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle, and assess blood flow. Typically considered an invasive procedure, coronary angiography involves the injection of a contrast dye into the coronary arteries through a catheter, which is threaded through blood vessels. X-ray imaging is then used to capture detailed images, known as angiograms, showing the structure and condition of the coronary arteries. Coronary angiography is a gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD), identifying blockages, narrowing, or other abnormalities. It helps healthcare professionals plan appropriate interventions, such as angioplasty or stent placement, to improve blood flow to the heart. While invasive, coronary angiography provides critical information for guiding treatment decisions and is often performed in conjunction with other cardiovascular tests.
H. Cardiac MRI
Cardiac MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides detailed images of the heart's structure, function, and blood flow. It can detect abnormalities such as heart muscle damage, inflammation, congenital heart defects, and tumors. Cardiac MRI is particularly useful for assessing conditions such as heart failure, myocarditis, and cardiomyopathy.